Gromov-Witten invariants
count (in a loose sense only) holomorphic maps from genus 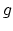 Riemann
surfaces to a variety
Riemann
surfaces to a variety 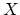 which pass through a given collection of
cycles on
which pass through a given collection of
cycles on 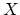 . In order to define these, we compactify the space of
maps from a variable pointed curve
. In order to define these, we compactify the space of
maps from a variable pointed curve 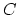 to
to 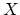 by allowing the domain
curve to degenerate to a nodal curve so that the corresponding map
always has finite automorphism group. For a fixed genus
by allowing the domain
curve to degenerate to a nodal curve so that the corresponding map
always has finite automorphism group. For a fixed genus 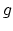 , image
homology class
, image
homology class 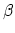 , and number of marked points
, and number of marked points 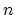 , this gives
the moduli space of stable maps
, this gives
the moduli space of stable maps
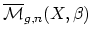 which is
typically a highly singular Deligne-Mumford stack. The Gromov-Witten
invariants of
which is
typically a highly singular Deligne-Mumford stack. The Gromov-Witten
invariants of 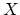 are given by integrals
where
are given by integrals
where
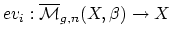 is evaluation at the
is evaluation at the 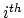 marked point and the
marked point and the 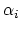 are elements of
are elements of
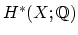 . An important point of the theory is that this
integral is defined via cap product with a distinguished homology
class known as the virtual fundamental class of
. An important point of the theory is that this
integral is defined via cap product with a distinguished homology
class known as the virtual fundamental class of
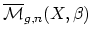 . The descendent Gromov-Witten Invariants
are obtained by inserting monomials in the Witten classes
. The descendent Gromov-Witten Invariants
are obtained by inserting monomials in the Witten classes 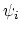 into the integral.
into the integral.
Jeffrey Herschel Giansiracusa
2005-06-27
![$\displaystyle \int_{[\overline{\mathcal{M}}_{g,n}(X,\beta)]^\mathrm{vir}}
ev_1^*(\alpha_1) \cdots ev_n^*(\alpha_n)
$](img70.png)